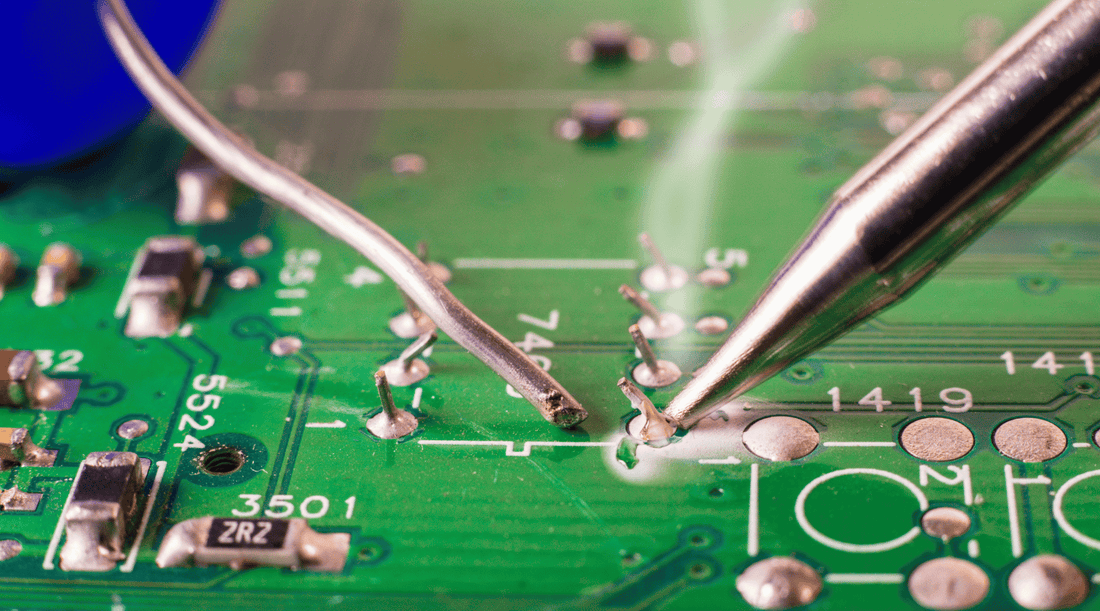
Circuit Board Soldering Iron - Your Essential Tool for Precise Electronics Assembly
Share
Circuit board soldering is a fundamental process in electronics assembly, allowing components to be securely connected to the board. One of the key tools in this process is the circuit board soldering iron. In this article, we will explore the different types of soldering irons and provide helpful suggestions to aid you in choosing the right soldering iron for your needs.
Introduction to Circuit Board Soldering Irons
Circuit board soldering irons play a critical role in the assembly and manufacturing of electronic devices. When it comes to creating strong, reliable connections between components and circuit boards, a soldering iron is an essential tool in the arsenal of any electronics enthusiast or professional.
In the world of electronics, soldering refers to the process of joining two or more metal components by melting a filler metal, known as solder, and allowing it to flow into the joint. Soldering is a fundamental technique used to create electrical and mechanical connections in circuit boards, ensuring the proper functioning of electronic devices.
A circuit board soldering iron is specifically designed to provide the necessary heat to melt the solder and create these connections. It consists of a handle, a heating element, a temperature control mechanism, and interchangeable tips. The handle is where the user holds the iron, while the heating element generates the heat needed to melt the solder. The temperature control mechanism allows the user to adjust and maintain the desired temperature, ensuring optimal soldering results.
The importance of circuit board soldering irons cannot be overstated. These tools are instrumental in the manufacturing of electronic devices, ranging from simple circuit boards for household gadgets to complex assemblies for advanced technologies. A well-executed soldering job ensures the proper flow of electrical signals, minimizes resistance, and enhances the overall performance and reliability of the circuit.
With advancements in technology and the increasing complexity of electronic devices, the demand for high-quality soldering irons has grown. Today, there is a wide variety of soldering irons available on the market, each offering unique features and capabilities to cater to different soldering needs.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the world of circuit board soldering irons, exploring the various types of soldering irons, factors to consider when choosing one, and essential tips and techniques for efficient soldering. By understanding the intricacies of soldering irons and acquiring the necessary skills, you will be well-equipped to handle soldering tasks and achieve professional-level results in your electronic projects.
Understanding Soldering Irons
Soldering irons consist of several key components, including a handle, heating element, temperature control mechanism, and interchangeable tips. These tips are responsible for transferring heat to the solder joint, making them a crucial factor in achieving successful soldering.
Different Types of Soldering Irons
- Basic Soldering Irons: These are the entry-level soldering irons, usually with a fixed wattage and temperature. They are affordable but lack temperature control.
- Temperature-Controlled Soldering Irons: These soldering irons offer adjustable temperature settings, allowing precise control over the heat applied to the solder joint. They are suitable for various applications and provide consistent results.
- Soldering Stations: Soldering stations consist of a base unit and a separate soldering iron. They provide more advanced features such as temperature stability, multiple tip options, and additional functionalities like digital displays or programmable presets.
- Cordless Soldering Irons: These soldering irons operate on battery power or butane gas powered and offer the flexibility of soldering without being tied to a power outlet. They are portable and convenient for on-the-go soldering task

Factors to Consider When Choosing a Circuit Board Soldering Iron
When selecting a soldering iron for circuit board assembly, several factors should be taken into account:
- Wattage and Temperature Range: The power output and temperature range of the soldering iron should match the specific requirements of the components being soldered.
- Heating Element Types: Different soldering irons use various heating elements, such as ceramic, PTC, or induction. Each has its advantages in terms of heat-up time, temperature stability, and durability.
- Tip Compatibility and Availability: It's essential to choose a soldering iron that offers a wide range of compatible tips. This ensures compatibility with different soldering tasks and easy availability for replacements.
- Ergonomics and User Comfort: A comfortable grip and ergonomic design are crucial for extended soldering sessions. Look for soldering irons with heat-resistant handles and lightweight construction.
- Additional Features and Accessories: Consider any extra features that might be beneficial, such as integrated LED lights, auto-sleep functionality, or the availability of soldering iron stands and holders.
Basic Soldering Iron Tips and Techniques

Before diving into the details of different soldering iron types, let's cover some basic soldering tips and techniques that apply to circuit board assembly.
Preparing the circuit board and components is crucial for successful soldering. Ensure the board is clean, free of dust or debris, and properly positioned. Components should be correctly oriented and aligned.
Choosing the right soldering iron tip is essential. For through-hole soldering, a chisel-shaped tip is commonly used, while for surface mount soldering, a finer, conical tip is preferred. The tip should be properly tinned and in good condition for optimal heat transfer.
When soldering, it's essential to apply heat to both the component lead and the pad on the circuit board. Allow the solder to flow freely and create a smooth, shiny joint. Excess solder and the formation of solder bridges should be avoided.
Benefits of Temperature-Controlled Soldering Irons
Temperature-controlled soldering irons offer several advantages over basic soldering irons:
- Precise Temperature Control: Different components have varying temperature requirements for proper soldering. Temperature-controlled irons allow you to set the exact temperature needed, ensuring consistent and reliable results.
- Avoiding Component Damage: Temperature control prevents overheating and thermal damage to sensitive components, such as integrated circuits or surface-mounted devices.
- Enhanced Soldering Quality and Reliability: With accurate temperature control, you can achieve better solder flow, improved wetting, and stronger joints, resulting in higher overall soldering quality and reliability.
Soldering Stations: A Versatile Solution
Soldering stations offer a comprehensive solution for circuit board soldering. They consist of a base unit and a separate soldering iron connected by a cable. Soldering stations provide several benefits:
- Temperature Stability: Soldering stations maintain a stable temperature throughout the soldering process, ensuring consistent results even during prolonged use.
- Multiple Tip Options: Soldering stations often come with interchangeable tips of different shapes and sizes. This versatility allows you to adapt to various soldering tasks and work with different component sizes.
- Additional Features for Advanced Soldering Tasks: Advanced soldering stations may offer features like digital temperature displays, programmable presets, or integrated soldering iron holders. These features enhance efficiency and convenience during soldering.
Cordless Soldering Irons: Portability and Convenience
For those who require portability and the freedom to solder without being tethered to a power outlet, cordless soldering irons are an excellent choice. They operate on rechargeable batteries and offer the following advantages:
- Portability and Flexibility: Cordless soldering irons allow you to work in various locations, including outdoor environments or tight spaces where access to a power source might be limited.
- Battery Technology and Runtime: Advancements in battery technology have improved the runtime and performance of cordless soldering irons. Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used, providing extended usage time and quick charging capabilities.
- Suitable Applications: Cordless soldering irons are suitable for small to medium-sized soldering tasks, making them ideal for hobbyists, field technicians, or situations where mobility is essential.
Tips for Efficient and Safe Soldering
Efficiency and safety should always be prioritized when using a soldering iron:
- Maintain a Clean Work Environment: Keep your work area clean and free of clutter. Proper organization reduces the risk of accidental damage or injury.
- Proper Handling and Storage of Soldering Irons: Always handle the soldering iron with care, using heat-resistant gloves if necessary. Store the iron in a dedicated holder or stand to prevent burns or accidental contact with flammable materials.
- Safety Precautions and Protective Equipment: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from splattering solder or stray components. Additionally, consider using fume extraction systems or working in a well-ventilated area to minimize exposure to soldering fumes.
Conclusion
A circuit board soldering iron is an essential tool for anyone involved in electronics assembly. It enables precise and reliable connections between components and circuit boards. By understanding the different types of soldering irons and considering factors such as wattage, temperature control, and additional features, you can choose the right soldering iron for your needs. Whether it's a basic soldering iron, a temperature-controlled station, or a cordless soldering iron, selecting the appropriate tool will contribute to successful and efficient soldering.
FAQs
Q: How do I choose the right wattage for a soldering iron?
A: To choose the right wattage, consider the size and thermal requirements of the components you'll be soldering. Smaller components typically require lower wattages, while larger or more heat-intensive components may require higher wattages.
Q: Can I use a soldering iron for other tasks besides circuit board soldering?
A: Absolutely! Soldering irons are versatile tools and can be used for various soldering tasks, such as jewelry making, wire repairs, or DIY electronics projects.
Q: What is the difference between leaded and lead-free soldering?
A: Leaded solder contains a small percentage of lead, which improves its melting and wetting properties. Lead-free solder, on the other hand, is composed of alloys without lead, conforming to environmental regulations. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements and regulations of your project.
Q: How often should I replace soldering iron tips?
A: Soldering iron tips wear out over time due to oxidation and repeated use. It's advisable to replace them when you notice signs of degradation, such as reduced heat transfer or poor solder flow. Regular cleaning and tinning can extend the life of the tip.
Q: Can I use a soldering iron without temperature control for circuit board soldering?
A: While it's possible to use a basic soldering iron without temperature control for circuit board soldering, it's more challenging to achieve consistent and reliable results. Temperature-controlled soldering irons provide greater precision and reduce the risk of damaging sensitive components.


